The Importance of Blood Donation
Blood donation constitutes a vital aspect of modern healthcare systems, functioning as a cornerstone for life-saving medical interventions and routine treatments across the globe. By providing a crucial supply of blood, donors play an integral role in the medical field, aiding in emergencies, facilitating surgical procedures, and enhancing the overall well-being of individuals with varying health conditions. Grasping the intricacies of the blood donation process can significantly alleviate apprehensions associated with it and foster greater participation among potential donors.
Eligibility Requirements
To maintain the safety and efficacy of blood donations, potential donors must adhere to specific eligibility criteria. The fundamental requirements typically dictate that individuals should be in sound health, a minimum of 17 years old, although those as young as 16 may donate with parental consent in some regions, and possess a body weight of at least 110 pounds (50 kg). Furthermore, it is pertinent for potential donors to consult with their local blood donation centers to understand the specific eligibility requirements applicable in their geographical location, as these can vary.
Registration and Health Screening
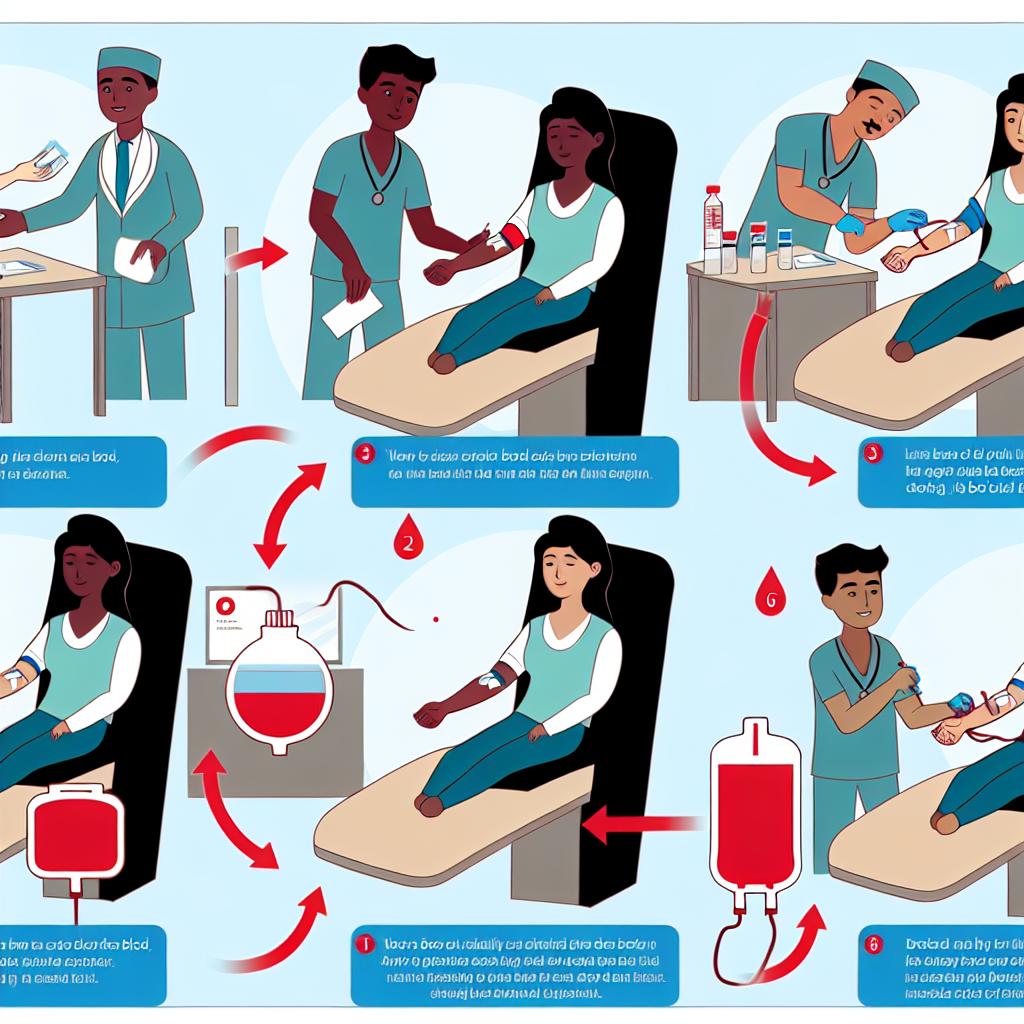
Upon arriving at the donation center, individuals partaking in the program must undergo a systematic registration process. This involves providing essential personal information such as their name, address, and a valid identification form. The structured nature of this process ensures the accountability and traceability of each blood donation. Subsequently, prospective donors proceed to a thorough health screening, during which a healthcare professional assesses vital signs such as blood pressure, pulse, and temperature. Additionally, a minor blood sample is taken to evaluate hemoglobin levels, ensuring individuals meet the necessary health standards to proceed with the donation.
Donation Procedure
Following the completion of the health screening, donors advance to the designated donation area, where the actual procedure commences. Typically lasting between 8 to 10 minutes, the donor remains in a reclined position as a sterile needle is gently inserted into a prominent vein, usually located in the arm. During this process, approximately one pint (about 470 ml) of blood is carefully collected. Continuous monitoring is conducted to ensure that donors remain both comfortable and safe throughout the procedure.
Types of Donations
There are several categories of blood donations, each serving distinct medical functions:
– Whole Blood Donation: Regarded as the most common donation method, it involves the collection of blood in its entirety.
– Platelet Donation: This focuses on harvesting platelets, crucial components for blood clotting. Such donations are particularly beneficial for cancer patients undergoing treatment.
– Plasma Donation: In this procedure, donors contribute plasma, the liquid constituent of blood, used predominantly in treatments targeting clotting disorders.
– Double Red Cell Donation: An automated process facilitates the extraction of two units of red cells, with the return of plasma and platelets to the donor.
Post-Donation Care
Upon completing their donation, individuals are encouraged to rest momentarily, typically for a few minutes, and revitalize themselves with snacks and fluids offered by the center. This helps in restoring blood volume and mitgating any feelings of lightheadedness. It is advisable for donors to refrain from engaging in vigorous physical activities for the remainder of the day and to sustain proper hydration levels.
Safety and Testing
Ensuring the safety of recipients is of paramount importance. Consequently, each donation undergoes meticulous testing for a spectrum of infectious diseases. Should any tests result in positive findings, donors are notified discreetly, maintaining confidentiality. The usage of sterile donation equipment, disposable after each use, further guarantees the safety of donors by effectively eliminating the risk of contracting infections.
Benefits of Donating Blood
Beyond its life-saving potentials, blood donation offers manifold benefits. For donors, the process serves as an opportunity for a health assessment courtesy of the exhaustive screening conducted. It enhances communal health by sustaining the blood supply necessary for medical treatments and, in certain instances, donating blood has been linked to reduced risks of specific health conditions. Esteemed organizations, such as the American Red Cross, continually provide invaluable insights into the positive impact and vast reach of blood donations on society.
Conclusion
The blood donation process embodies a relatively straightforward and secure medical practice that holds immense significance within the broader healthcare spectrum. By fostering a comprehensive understanding of the procedure and underscoring the profound impact of such donations, it becomes possible to galvanize more individuals into participating. Ultimately, this increased participation contributes to a heightened availability of this quintessential healthcare resource necessary for the preservation and enhancement of human lives.